研究目标
机器的智能化提升了其自主性能力,冲击了传统人机系统中的人机静态刚性边界。拟定量/准定量刻画机器的自主性、不确定性,界定新型人机系统中的人机柔性边界,探索可行的人机动态切换准则和方法,为相关应用提供理论指导。
主要研究内容
- 人机融合系统中机器智能的机理分析、自主能力评估和不确定性来源分析
- 人机融合系统中人的认知不确定性对融合智能的影响分析
- 人机融合系统中面向融合和切换的科学研究框架构建
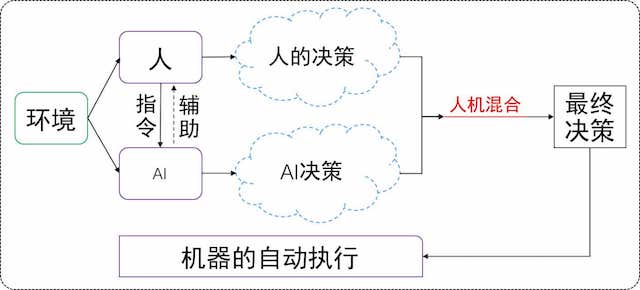
基本研究框架
相关阅读
研究成果
Theses
-
基于人类决策有效性的人机混合决策方法研究
游诗艺
中国科学技术大学, 合肥
2022
[Abs]
[pdf]
随着人工智能技术的发展,机器的自主能力不断地提高,智能机器在各行各 业的应用和发展日益深入。在此进程中,不可避免地会遇到智能机器无法应对 实际任务的复杂性和不可预测性的情况,许多系统在未来仍将需要人类在监督、 目标设定、应急响应等方面与机器进行持续、密切的交互,研究此种场景下如何 混合人类决策和机器决策以达到更好的决策效果也因此尤为重要和有意义。 在人机混合决策中,人类决策是否有效,即人的决策是否促进任务的完成并 有效地反映人类的真实意图,从两方面影响着最终的决策性能。一方面在于一方 决策失效将导致混合性能的下降;另一方面在于智能机器常常无法直接得知人 的意图,而需先根据人类决策推测意图,再做出决策辅助人完成该意图,人类决 策的失效可能导致意图推理的失效,进而导致人机混合决策方法的失效和任务 失败。因此本文以人机混合决策方法为研究对象,基于人类决策的有效性,从人 类决策全时有效和人类决策非全时有效两个方面展开研究,提出基于强化学习 的人机混合决策方法来改善决策性能。本文的研究工作主要包括以下两个方面: (1)针对人类决策全时有效的情况,提出一种基于最小干预原则的人机混合 决策方法,在优化整体系统性能的基础上,进一步考虑人对于人机系统满意度的 相关指标。通过将最小干预原则引入人机混合决策,设置人机决策融合的自适应 阈值,该方法能够以最小程度的干预为人类提供最大程度的帮助,并能在实时变 化的环境中保持最优,同时提升和改善系统性能和人类满意度两类指标,为后续 的优化设计方案提供基础性方法。 (2)针对人类决策非全时有效的情况,提出一种基于人类决策有效性评估机 制的人机混合决策方法,以避免人的无效决策损害系统性能。通过利用强化学习 算法判断人类决策的有效性,识别人的意图是否改变,该方法能够在人类决策无 效时由机器单独完成任务,使得系统在人类决策非全时有效的情况下,仍能完成 正确的任务目标,有效提升了人机混合决策质量和系统性能。
-
人的介入提升深度学习算法精度的方法及其实例研究
花婷婷
浙江工业大学, 杭州
2021
[Abs]
[pdf]
现实中许多智能应用往往并不具备获取足量、高质的训练数据的天然条件, 这一定程度上影响了深度学习算法所能达到的精度;而与此同时,众多领域却 对其应用精度有着极高的现实要求:这两方面的原因使得在深度学习的基本框 架外寻求精度的提升成为近些年的一个重要关注点。 在这一领域中,有研究者发现人的介入可能是提升深度学习应用精度的一 种可行途径。该方法借用人机系统中介入思想以解决非人机系统中的相关技术 难题,即在机器算法有误时允许人的介入来提升整体系统的应用精度。 本文基于典型实例研究了人的介入提升深度学习应用精度的两种方法,即 人的分歧介入方法和人的融合介入方法。前者方法考虑在多个算法产生预测分 歧之处,决策权将交由经验丰富的人直接控制;后者则更多的考虑寻求基于普 通用户介入下的可操作性,在算法的预测置信度较低时,利用人在感知层面的 信息传输实现对算法错误决策的可靠修正。具体研究工作如下: (1)面对珍珠分拣任务的经济效益与质量需求的高标准,提出了一种人的 分歧介入方法,该方法在公开珍珠数据集上,以 4.1%的额外人工成本提升了近 4%的珍珠分拣精度,较大程度上解决了现有珍珠分拣精度不高的问题。本实验 为珍珠分拣系统提供额外的冗余 AI 算法,通过比对多个算法的预测结果,在产 生分歧之处作为仲裁机制来判断系统的预测是否出错,以此驱动珍珠分拣人员 的介入。最终使用定义分歧准确指数和额外成本指数这两大性能评价指标来评 估设计系统的整体性能。 (2)针对野生鸟类资源信息识别对整个社会生态价值和经济价值的高需求, 提出了一种人的融合介入方法,该方法在公开基准 CUB-200-2011 数据集上, 以最小化的人工成本将鸟类细粒度图像识别精度提升到 93.8%,实现了目前机 器视觉算法在细粒度鸟类图像识别难题上的突破。借用二分类模型评估思想, 本实验通过分析算法的 ROC 指标,选取类别预测最优阈值作为仲裁机制,当算 法的预测置信度低于阈值条件即作为人的介入时机。并通过将人的视觉信息与 嵌入的鸟类知识图谱信息融合为算法提供更具信息性的特征判断实现可靠分类。
-
基于机器视觉的驾驶员注意力检测系统设计
唐敏
浙江工业大学, 杭州
2021
[Abs]
[pdf]
驾驶员注意力不集中是指驾驶员的注意力被一些分心驾驶行为所分散从而 不集中。车辆驾驶过程中的注意力分散行为将会使得驾驶员的反应过程被拉长, 进而使得驾驶员对车辆能否安全行驶的判断能力和对突发情况的反应能力降低, 极易引起交通安全事故。近年来,驾驶员注意力检测已经越来越多地受到大家 的关注。 本文针对驾驶员注意力检测场景,设计了基于机器视觉的驾驶员注意力检 测系统,进行了驾驶员注意力检测系统的软硬件设计,设计的基于多粒度特征 和中间层特征的 MGMN 算法在现有的公开的分心驾驶数据集中取得了更高的精 确度,设计的硬件系统成本较低并且在真实场景实验中也有着较高的实用性。 本文的主要工作有以下两个方面: (1) 设计了基于多粒度特征和中间层特征的驾驶员注意力检测算法,该算法 具有精度高、特征提取丰富且准确的特点。考虑到驾驶员在驾驶时头部和手部 都处于图像的相对固定的位置,并且头部一般处于图片的上方,手部一般处于 图片的中下方。如果可以针对驾驶图像的每一部分进行学习,提取每一部分特 有的特征,本文在 ResNet50 模型中加入了多粒度特征提取部分,该部分有全局 分支、二分支和三分支三部分,共同提取驾驶图像的全局和局部特征。同时又 抽取了驾驶图像的中间层特征,中间层包含了丰富的图像特征,最后将多粒度 特征和中间层特征一起输入到 Softmax 损失函数中,设计出了 MGMN 算法。 MGMN 算法无论是在现有的分心驾驶检测公开数据集上还是在自建数据集上都 有着更高的精确度和较短的运行时间。 (2)设计了“树莓派 +远程服务器”的驾驶员注意力检测系统。 采用“树莓 派+远程服务器”的结构,通过局域网将树莓派与远程服务器相连接,具有较高 的信息传输速率,树莓派与服务器之间采用 Socket 通信方式进行通信,做到终 端与服务器之间的信息的准确传输。同时采用成本低、体积小、可靠性高的树 莓派作为驾驶图像实时采集终端,采用配置高、运行效率高的服务器作为状态 判别的设备,降低了设计成本,实现了对驾驶员注意力状态实时的高精度检测。
-
面向人机序贯决策的混合智能方法研究
张倩倩
中国科学技术大学, 合肥
2021
[Abs]
[pdf]
随着人工智能技术的发展,机器智能得到不断的提高,随之而来的则是机 器智能得以在各行各业应用发展。在此进程中,不可避免的会遇到机器自主性 不足以解决本身该由人类解决或者人类必须参与决策的情况,考虑此种场景下 人类智能和机器智能共同作用的决策问题则显得尤为重要和有意义。更具体地, 序贯决策问题作为一类具有时序性和多阶段性的动态决策问题,其发展与当下 人工智能时代下的工程应用、生产生活等领域息息相关。人的作用体现在序贯决 策问题的两方面,一则,人本身属于序贯决策问题模型中的一部分,即该类问题 是离不开人的如微创外科手术等;二则,人的相关信息不体现在序贯决策问题模 型中,而是因人独特的认知能力使得其可以出现在问题的求解办法中,达到改善 问题求解的目的如人对机器搜救系统的引导等,我们将上述两种场景统称为 “人 机序贯决策问题”。 针对人机序贯决策问题,由于人类智能和机器智能本质上的区别,数学表达 上的巨大差异,使得人和机器共同作用于问题求解时,不可避免的因为协调原因 造成决策质量不高甚至决策失误的现象。然而直接应用传统人机系统的控制算 法不能有效处理这些问题,从而引起机器代理失效,人力浪费,甚至还会造成决 策系统性能恶化甚至崩溃。因此,亟需设计有效的人机混合智能算法来解决这些 问题。本文以人机序贯决策问题为研究对象,围绕人机混合智能控制中的决策权 限划分、介入控制触发切换时机和共享控制混合人机决策动作程度三个问题展 开研究,旨在提出有效的人机混合智能算法来改善提升人机序贯决策问题的求 解。本文的研究工作主要包括以下几个方面: 1. 提出了基于强化学习方法的人机混合智能控制框架。通过将机器代理的决 策和人类的决策以可信性和安全性为评价指标进行仲裁选择,以确定更优 的待执行决策动作。同时考虑了基于模型的强化学习子系统和基于无模型 的强化学习子系统,为适应广泛的序贯决策应用场景提供了更多可能。 2. 针对人机序贯决策中的介入控制问题,提出了自主性及自主性边界的概念, 通过将自主性边界的求解形式化为与任务目标相关的常规优化问题进行讨 论判定,优化介入控制的控制方案和算法,实现人机序贯决策中人介入机 器场景和机器介入人场景下的决策性能提升。 3. 针对人机序贯决策中的共享控制问题,提出了基于自主性边界的混合参数 优化设计方案,通过自适应调节混合参数大小直接影响最终待执行动作的 生成。考虑了人机动作的融合程度,使得最优解在人的动作空间和机器的 动作空间所共同张成的扩展空间中出现,为决策质量的提升提供了扩展空间。 4. 针对介入控制和共享控制中所估计的自主性边界值可能存在单值估计不准 确的问题,提出了基于贝叶斯神经网络的不确定性估计办法,获得自主性 边界的概率分布信息并用于决策动作生成,利用自主性边界的不确定性优 化设计人机混合智能算法,既使得决策动作的优化存在更多选择,也更加 符合人们对决策边界的模糊性思考。 综上所述,本文面向人机序贯决策对混合智能算法所面临的问题进行了系 统性的研究,创新性地提出了对应的解决方案,推动了人机序贯决策求解和混合 智能算法的进一步发展。
-
融合人的认知模型的模糊支持向量机算法及其应用
赵丽丽
浙江工业大学, 杭州
2021
[pdf]
-
程序员的疲劳状态检测方法
孙悦铖
2020
[Abs]
[pdf]
随着计算机的发明和广泛应用,它早就成为了人类社会中的重要一环。而程 序员作为开发以及维护计算机程序的专业人员,该人群的数量庞大并仍在逐年增 加。但程序员的工作状态以及工作强度导致他们极易进入疲劳状态,长期的疲劳 会引起工作效率下降、危害身心健康。准确检测其疲劳状态,进行适当的提醒可 对程序员的健康起到一定的保护作用。 传统的疲劳检测技术并不非常契合程序员的疲劳状态检测情况。本文主要通 过神经网络技术对判别程序员的疲劳状态方法进行探究和尝试,并实现具有检测 功能的程序。 论文的主要工作如下: 1、简述课题研究背景和研究现状,简要介绍了疲劳检测产生并发展至今的 各种主要技术,分析其对本课题的适用性。 2、概述神经网络结构原理,探究一些经典的图像分类神经网络。确立使用神 经网络技术的疲劳检测方案。 3、自建脸部状态的疲劳检测数据集,对嘴部和眼部的疲劳特征有较好的反 应。提出并实验了预先对所需特征进行切割凸显来保证识别准确的方法。 4、编写疲劳检测程序,基本实现了应用神经网络对人疲劳检测的功能。可通 过对眨眼和哈欠等脸部状态识别,判读是否疲劳,并在检测到疲劳状态后 进行提醒 本文预期目标为尝试检测方法,在程序中实现对程序员的疲劳状态检测。通 过毕设期间的努力达成了该目标,但仍有不足之处:自建数据集的丰富度不足; 检测程序的精度尚有提升空间。这些都应该是在未来进行改善的点。
-
基于 Arguing Machines 框架的人机协作方法研究
严家淦
2020
[Abs]
[pdf]
随着人工智能技术的快速发展,大量企业已经在各自领域中广泛应用人工智 能技术,其中包括一些低容错领域,例如医学诊断系统、无人驾驶系统、智能医 学影像领域等。人工智能在低容错领域的错误决策会严重影响人类的生命安全和 财产安全,所以低容错领域对人工智能系统应用的准确程度的要求更为严格。 目前提升人工智能系统的准确率主要有两种途径。(1)单方面提升系统准 确程度达到可接受性能水平。(2)将人工智能系统与辅助其运行的人工监督相 结合,使人机协作的系统达到可接受的性能水平。前者专注于机器学习,但是单 方面提升系统准确度需要对机器学习有更深入的研究,且研究难度较大、研究进 展较小;第二种办法通过人机协作的方式来提升准确程度,本文具体使用人机协 作中的 Arguing machines 框架。 本文的研究内容是验证 Arguing machines 框架提高系统准确程度的能力。本 次验证工作具体针对珍珠分拣领域,将 ResNet-50 和 SE-ResNet-50 分别设置成为 主副系统,当这两个系统对珍珠图像进行识别分类的输出决策产生分歧时,将分 歧图像交给人工鉴别,从而在花费少量人工成本情况下提升系统准确程度。论文 的主要工作如下: 1. 设计基于珍珠分拣该应用场景的系统模型选取方案:将 ResNet-50 设置成 为主系统,SE-ResNet-50 设置成为辅助系统。详细介绍两个模型的结构与选取原 因。 2. 进行基于珍珠分拣领域的 Arguing machines 框架的神经网络搭建,在珍珠 图像数据集中达到 96.28%的准确度,验证了 Arguing machines 框架拥有提高系 统准确度的能力。 3. 提出并完成一系列框架优化工作:(1)将 4 种卷积神经网络排列组合进 行系统性能对照实验。(2)提取单模型训练过程中不同训练结果搭建框架进行 验证工作。(3)提升 Arguing machines 框架所需模型数,验证基于三模型框架 的性能水平。
-
基于马尔可夫决策过程的人机共享自治方法研究
赵丹波
2020
[Abs]
[pdf]
在许多领域中,交互式系统要么为我们自主地做出决策,要么为我们提供决 策权并发挥支持作用。但是,许多设置例如在教育或工作场所中的设置,受益于 在用户和系统之间共享这种自主权,并因此受益于随着时间的推移而适应他们的 系统。针对钢琴教学,传统的视频教学虽然节省了人力更为方便,但是重复的视 频容易使用户失去专注,无法保证学习的效率;将控制权交予用户又会使得操作 过于繁琐。所以需要设计交互式共享自主的钢琴教学系统。 在本文中,主要研究的是基于马尔可夫决策过程的人机共享自治的方法来更 好地实现特定目标,我们设计了一种用于钢琴教学的交互式共享自主系统,可播 放乐曲的不同片段,供学生模仿和练习。运用部分可观察的马尔可夫决策过程, 以人的性能和注意力作为可观察的状态变量,使用二进制值来测量状态变量,在 动态贝叶斯网络中对这些变量之间的过渡进行建模形成信念,推测用户的期望, 从而来进行自治权的授予。论文的主要工作如下: 1. 叙述论文的研究背景以及研究意义,介绍人机交互系统以及人机关系中 人的作用。 2. 运用 POMDP 决策方法可以在不确定性环境和条件下做决策的特性,基 于 POMDP 对人机交互式系统进行建模研究,构造出一种从人机系统的 人的可观测因素中去推断系统中人的未知的内部状态形成信念的方法 , 并运用这种方法对人机关系的自治权归属进行判别。 3. 改造合适的 MDP 模型建立于钢琴教学的交互式共享自主系统,通过对系 统自治权是控制实现系统功能的最优化 。并通过仿真实验对钢琴教学系 统的有效性进行验证。
-
人机系统中人的认知偏差的识别方法研究
吴芳
2019
[Abs]
[pdf]
随着科学技术的进步以及人们对生产发展的各方面要求越来越高,人机系统的角色 越来越丰富。人机系统是由人和机器构成并依赖于人机之间相互作用而完成一定功能的 系统,人机系统的性能取决于人和机器两部分,在本文中我们假定机器是完美的,只考 虑人的行为对系统性能的影响。当人机系统处于特定的目标、特定的环境下,人可能会 比较容易产生某种内部异常或认知偏差,导致错误的决策,影响人机系统的性能。 本文的研究内容是识别人机系统中人的认知偏差,本文将认知偏差从心理学上的定 义扩展到包含生理、心理两部分的内部状态异常。由于人机系统中的人产生的内部异常 一般会影响到人机系统的输出,因此我们从人机系统的输出数据检测人的内部状态,判 断人是否产生了异常。论文的主要工作如下: 1. 综述论文研究背景及意义,介绍对人机系统中的人以及对人和机器协同控制的 研究现状。 2. 借鉴了在不确定性条件下做决策的 POMDP 方法,基于 POMDP 对人机系统进 行建模,构造了一种从人机系统的输出数据的特点中去推断系统中人的内部状态是否异 常的方法。 3. 基于常见的人驾驶汽车场景下的人机系统设置仿真实验,验证本文提出的方法 的有效性。
Journal Articles
-
Traded Control of Human–Machine Systems for Sequential Decision-Making Based on Reinforcement Learning
Qianqian Zhang,
Yu Kang,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
Pengfei Li,
and Shiyi You
IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell.
2022
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
Sequential decision-making (SDM) is a common type of decision-making problem with sequential and multistage characteristics. Among them, the learning and updating of policy are the main challenges in solving SDM problems. Unlike previous machine autonomy driven by artificial intelligence alone, we improve the control performance of SDM tasks by combining human intelligence and machine intelligence. Specifically, this article presents a paradigm of a human–machine traded control systems based on reinforcement learning methods to optimize the solution process of sequential decision problems. By designing the idea of autonomous boundary and credibility assessment, we enable humans and machines at the decision-making level of the systems to collaborate more effectively. And the arbitration in the humanmachine traded control systems introduces the Bayesian neural network and the dropout mechanism to consider the uncertainty and security constraints. Finally, experiments involving machine traded control, human traded control were implemented. The preliminary experimental results of this article show that our traded control method improves decision-making performance and verifies the effectiveness for SDM problems.
-
Emotion-Movement Relationship: A Study Using Functional Brain Network and Cortico-Muscular Coupling
Xugang Xi,
Qun Tao,
Jingqi Li,
Wanzeng Kong,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
Huijiao Wang,
and Junhong Wang
Journal of Neuroscience Methods
2021
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
Background: Emotions play a crucial role in human communication and affect all aspects of human life. However, to date, there have been few studies conducted on how movements under different emotions influence human brain activity and cortico-muscular coupling (CMC). New methods: In this study, for the first time, electroencephalogram (EEG) and electromyogram physiological electrical signals were used to explore this relationship. We performed frequency domain and nonlinear dy namics analyses on EEG signals and used transfer entropy to explore the CMC associated with the emotionmovement relationship. To study the transmission of information between different brain regions, we also constructed a functional brain network and calculated various network metrics using graph theory. Results: We found that, compared with a neutral emotional state, movements made during happy and sad emotions had increased CMC strength and EEG power and complexity. The functional brain network metrics of these three emotional states were also different. Comparison with existing methods: Much of the emotion-movement relationship research has been based on subjective expression and external performance. Our research method, however, focused on the processing of physiological electrical signals, which contain a wealth of information and can objectively reveal the inner mechanisms of the emotion-movement relationship. Conclusions: Different emotional states can have a significant influence on human movement. This study presents a detailed introduction to brain activity and CMC.
-
Effect of Muscle Fatigue on the Cortical-Muscle Network: A Combined Electroencephalogram and Electromyogram Study
Xugang Xi,
Shaojun Pi,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
Huijiao Wang,
and Zhizeng Luo
Brain Research
2021
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
Electroencephalogram (EEG) and electromyogram (EMG) signals during motion control reflect the interaction between the cortex and muscle. Therefore, dynamic information regarding the cortical-muscle system is of significance for the evaluation of muscle fatigue. We treated the cortex and muscle as a whole system and then applied graph theory and symbolic transfer entropy to establish an effective cortical-muscle network in the beta band (12–30 Hz) and the gamma band (30–45 Hz). Ten healthy volunteers were recruited to participate in the isometric contraction at the level of 30% maximal voluntary contraction. Pre- and post-fatigue EEG and EMG data were recorded. According to the Borg scale, only data with an index greater than 14<19 were selected as fatigue data. The results show that after muscle fatigue: (1) the decrease in the force-generating capacity leads to an increase in STE of the cortical-muscle system; (2) increases of dynamic forces in fatigue leads to a shift from the beta band to gamma band in the activity of the cortical-muscle network; (3) the areas of the frontal and parietal lobes involved in muscle activation within the ipsilateral hemibrain have a compensatory role. Classification based on support vector machine algorithm showed that the accuracy is improved compared to the brain network. These results illustrate the regulation mechanism of the cortical-muscle system during the development of muscle fatigue, and reveal the great potential of the cortical-muscle network in analyzing motor tasks.
-
Construction and Analysis of Cortical–Muscular Functional Network Based on Eeg-Emg Coherence Using Wavelet Coherence
Xugang Xi,
Ziyang Sun,
Xian Hua,
Changmin Yuan,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
Seyed M. Miran,
Zhizeng Luo,
and Zhong Lü
Neurocomputing
2021
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
Research on the brain functional network is important in understanding the normal function of the brain and diagnosing neuropsychiatric diseases. Inspired by the brain functional network, we constructed a cortical–muscular functional network using electroencephalography and electromyography to explore the motion control mechanism of the central nervous system and understand the organization and coordination mechanisms of limb motion control. In the process of constructing the network, 12 signal acquisition channels were selected as nodes, and the wavelet coherence is used as the index of connection between network nodes. Based on the original network, we used a fixed weighted edge and threshold methods to remove weak weighted edges and compare the performance of the two methods. The experimental results showed that the constructed network had a higher clustering coefficient, and the smaller characteristic path length indicated a small-world characteristic. At the same time, the weighted characteristic path length and weighted clustering coefficient of the functional network simplified by the threshold method can show promising classification accuracy under Fisher and artificial neural network.
-
浅谈控制中的共享信息和共享自主
赵云波,
康宇,
and 朱进
系统与控制纵横
2021
[Abs]
[pdf]
控制系统是由受控对象、传感器、控制器、 执行器等不同组件有机构成的随时间演化的一 个整体,控制理论研究控制系统的动态行为,和前馈、反馈等控制机制对系统动态行为的改造, 而控制工程则依托控制理论解决各种实际应用 领域中的控制问题。与绝大多数信息和工程技术 不同的是,控制是一种使能技术,并不局限于某 一特定应用领域,而是在现代科技的几乎所有方 方面面都起着某种关键基础性作用。 从宏大的技术发展的角度来看,控制的发展 与人类历史的技术变革相伴相生,而技术变革也 对控制提供了不同的机遇和相伴而来的要求和 挑战。首先,起于 19 世纪末的工业革命掀起了 轰轰烈烈的以机器替代人的劳动的革命,在其中 控制赋能的自动化起到了关键基础性的作用;其 次,伴随着始于上个世纪末、至今仍方兴未艾的 信息革命的发展,远程、大规模、网络化的控制 系统和自动化应用极大的拓展了控制的版图; 最后,近些年才重新兴盛起来但潜力无限的人工 智能(Artificial Intelligence, AI)技术,则带来了 变革性的机器自主性革命,将控制系统的研究带 入了一个崭新的领域。 本文试图简单讨论信息革命和 AI 自主革命 带给控制的若干机遇和挑战,特别的,分别关注 其中的“共享信息”和“共享自主”控制范式。 本文并不打算对这两个相关领域给出详尽的理 论和方法上的介绍,而是较为科普性质的,目的 是通过对问题的来源和其重要性的讨论,希望能 够吸引更多研究者投入到这两个相关联领域的 研究当中来。
-
Enhanced EEG–EMG Coherence Analysis Based on Hand Movements
Xugang Xi,
Cunbin Ma,
Changmin Yuan,
Seyed M. Miran,
Xian Hua,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
and Zhizeng Luo
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control
2020
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
Electroencephalogram (EEG)–electromyogram (EMG) coherence analysis is an effective method for examining the functional connection between brain and muscles. An improved coherence approach is proposed in this study to enhance the estimation of EEG–EMG coherence. First, we sampled the synchronous EEG signal based on the burst points of the EMG signal. Then, a moving average of the sampled EEG by using a window function is performed before the EEG is sampled again on the basis of the EMG burst points. The EEG signals are reassembled to effectively reflect the muscle motions. Finally, the estimation of the EEG–EMG coherence is computed by using magnitude square coherence (MSC) and wavelet coherence. The coherence characteristics of the different autonomous movements in the -band and band are analyzed to verify the reliability of the method. Results show that our proposed method can remarkably enhance EEG–EMG coherence estimation regardless of using either MSC or wavelet coherence. The results of coherence analysis not only can correctly reflect the coupling relationship between the cortex and the muscles but can also distinguish the EEG–EMG coherences of the different autonomous movements.
-
sEMG-MMG State-Space Model for the Continuous Estimation of Multijoint Angle
Xu-Gang Xi,
Chen Yang,
Seyed M Miran,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
Shuliang Lin,
and Zhizeng Luo
Complexity
2020
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
Continuous joint angle estimation plays an important role in motion intention recognition and rehabilitation training. In this study, a surface electromyography- (sEMG-) mechanomyography (MMG) state-space model is proposed to estimate continuous multijoint movements from sEMG and MMG signals accurately. The model combines forward dynamics with a Hill-based muscle model that estimates joint torque only in a nonfeedback form, making the extended model capable of predicting the multijoint motion directly. The sEMG and MMG features, including the Wilson amplitude and permutation entropy, are then extracted to construct a measurement equation to reduce system error and external disturbances. Using the proposed model, a closed-loop prediction-correction approach, unscented particle filtering, is used to estimate the joint angle from sEMG and MMG signals. Comprehensive experiments are conducted on the human elbow and shoulder joint, and remarkable improvements are demonstrated compared with conventional methods.
-
Facial Expression Distribution Prediction Based on Surface Electromyography
Xugang Xi,
Yan Zhang,
Xian Hua,
Seyed M. Miran,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
and Zhizeng Luo
Expert Systems with Applications
2020
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
Facial expression recognition plays an important role in research on human-computer interaction. The common facial expressions are mixtures of six basic emotions: anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, and surprise. The current study, however, focused on a single basic emotion on the basis of physiological signals. We proposed emotion distribution learning (EDL) based on surface electromyography (sEMG) for predicting the intensities of basic emotions. We recorded the sEMG signals from the depressor supercilii, zygomaticus major, frontalis medial, and depressor anguli oris muscles. Six features were extracted in the frequency, time, time-frequency, and entropy domains. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to select the most representative features for prediction. The key idea of EDL is to learn a function that maps the PCA-selected features to the facial expression distributions such that the special description degrees of all basic emotions for an emotion can be learned by EDL. Simultaneously, Jeffrey’s divergence considered the relationship between different basic emotions. The performance of EDL was compared with that of multilabel learning based on PCA-selected features. Predicted results were measured by six indices, which could reflect the distance or similarity degree between distributions. We conducted an experiment on six different emotion distributions. Experimental results show that the EDL can predict the facial expression distribution more accurately than the other methods.
-
Feature Extraction of Surface Electromyography Based on Improved Small-World Leaky Echo State Network
Xu-Gang Xi,
Wenjun Jiang,
Seyed M Miran,
Xian Hua,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
Chen Yang,
and Zhizeng Luo
Neural Computation
2020
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
Surface electromyography (sEMG) is an electrophysiological reflection of skeletal muscle contractile activity that can directly reflect neuromuscular activity. It has been a matter of research to investigate feature extraction methods of sEMG signals. In this letter, we propose a feature extraction method of sEMG signals based on the improved small-world leaky echo state network (ISWLESN). The reservoir of leaky echo state network (LESN) is connected by a random network. First, we improved the reservoir of the echo state network (ESN) by these networks and used edge-added probability to improve these networks. That idea enhances the adaptability of the reservoir, the generalization ability, and the stability of ESN. Then we obtained the output weight of the network through training and used it as features. We recorded the sEMG signals during different activities: falling, walking, sitting, squatting, going upstairs, and going downstairs. Afterward, we extracted corresponding features by ISWLESN and used principal component analysis for dimension reduction. At the end, scatter plot, the class separability index, and the Davies-Bouldin index were used to assess the performance of features. The results showed that the ISWLESN clustering performance was better than those of LESN and ESN. By support vector machine, it was also revealed that the performance of ISWLESN for classifying the activities was better than those of ESN and LESN.
-
Surface Electromyography-Based Daily Activity Recognition Using Wavelet Coherence Coefficient and Support Vector Machine
Xu-Gang Xi,
Chen Yang,
Jiahao Shi,
Zhizeng Luo,
and Yun-Bo Zhao
Neural Processing Letters
2019
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
Daily activity monitoring plays an important role among frail or elderly people and has caught attention. Surface electromyography (sEMG) can extract the feature of activity, but it is not stable because of electrode displacement, postural changes, and individual- dependent features, such as the condition of muscles, subcutaneous fat, and skin surface. To effectively extract the feature of sEMG signal, we proposed a new method of feature extraction based on coherence analysis. The sEMG signals were recorded from gastrocne- mius, tibialis anterior, rectus femoris, and semitendinosus. After de-noising, sEMG signals were decomposed into 32-scale by wavelet transformation, and their wavelet coefficients were employed to calculate wavelet coherence coefficients (WCC). We employed T test to find out if the coherence between sEMG signals was statistically different among six activi- ties. The 32nd scale WCC of RF–ST and ST–TA as eigenvector was entered into the sup- port vector machine (SVM). The six activities, namely, standing, walking, running, stair- ascending, stair-descending, and falling, were successfully identified by the WCC feature with the SVM classifier.
-
Denoising of Surface Electromyogram Based on Complementary Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and Improved Interval Thresholding
Xu-Gang Xi,
Yan Zhang,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
Qingshan She,
and Zhizeng Luo
Review of Scientific Instruments
2019
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
Surface electromyogram (sEMG) signals are physiological signals that are widely applied in certain fields. However, sEMG signals are frequently corrupted by noise, which can lead to catastrophic consequences. A novel scheme based on complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition (CEEMD), improved interval thresholding (IT), and component correlation analysis is developed in this study to reduce noise contamination. To solve the problem of losing desired information from sEMG, an sEMG signal is first decomposed using CEEMD to obtain intrinsic mode functions (IMFs). Subsequently, IMFs are selected via component correlation analysis, which is a measure used to select relevant modes. Thus, each selected IMF is modified through improved IT. Finally, the sEMG signal is reconstructed using the processed and residual IMFs. Root-mean-square error (RMSE) and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) are introduced as evaluation criteria for the sEMG signal from the standard database. With SNR varying from 1 dB to 25 dB, the...
Conference Articles
-
Adaptive Arbitration for Minimal Intervention Shared Control via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Shiyi You,
Yu Kang,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
and Qianqian Zhang
In 2021 China Automation Congress (CAC)
2021
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
In shared control, humans and intelligent robots jointly complete real-time control tasks with their complementary capabilities for improved performance unavailable by neither side on its own, which is attracting more and more attentions in recent years. Arbitration, as an indispensable part of shared control, determines how control authority is allocated between the human and robot, and the definition of that policy has always been one of the fundamental problems. In this paper, we propose an adaptive arbitration method for shared control systems, which minimizes the deviation from the human inputs while ensuring the system performance based on deep reinforcement learning. We provide humans the maximum assistance with the minimal intervention, in order to balance human’s need for control authority and need for performance. We apply our method to real-time control tasks, and the results show that our method achieves high task success rate and shorter task completion time with less human workload, while maintaining higher human satisfaction.
-
Detection of Distracted Driving Based on Multi-Granularity and Middle-Level Features
Min Tang,
Fang Wu,
Li-Li Zhao,
Qi-Peng Liang,
Jian-Wu Lin,
and Yun-Bo Zhao
In 2020 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC)
2020
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
A so-called MGMN (Multiple-GranularityMiddle Network) algorithm is proposed to improve the detection accuracy of distracted driving, based on multigranularity features and middle-level features. The algorithm is derived from the ResNet50 neural network and is the first time to use multi-granularity features and mid-level features of images in the field of distracted driving detection. The multigranularity feature extraction module consists of three branches: the global branch to learn the global features without local information, the second branch to divide the image level into two parts and later to learn the local features of the upper and lower parts, and the third branch to divide the image level into three parts, and later to learn the local features of the upper, middle and lower parts. By extracting the features of the middle layer of the image, the feature extraction of the algorithm is enriched. While the multi-granularity features are individually input to the cross-entropy loss function, the multi-granularity features of the image and the middle-level features are combined and input into the cross-entropy loss function. The proposed algorithm has an accuracy of 99.8% on the dataset "Districted-DriverDetection" published by State Farm Company, which is 1.5% to 3% higher than existing algorithms, and an improved accuracy of 98.7% on the dataset "AUC-Districted-Driver-Detection".
-
Autonomous Boundary of Human-Machine Collaboration System Based on Reinforcement Learning
Qianqian Zhang,
Yun-Bo Zhao ,
and Yu Kang
In 2020 Australian and New Zealand Control Conference (ANZCC)
2020
[Abs]
[doi]
[pdf]
This paper provides a human-machine collaborative control framework, including artificial intelligence decision systems, human-level control, arbiter judgment, and learning of autonomous boundary, so that human suggestions are incorporated into the training process of decisions, assisting agents to learn quickly control decision tasks. Based on the model-free deep reinforcement learning algorithm HITL-AC, the human feedback (reward or punishment) is connected with the reward of the agent, so that the agent continuously tries to find a better boundary during the system’s operation, avoiding defects of pre-fixed boundary. This formulation improves the data efficiency of reinforcement learning and plays a guiding role in seeking human intervention when the agent is in an uncertain environmental state during the test use phase. The fourth section of the paper gives a training demonstration of the bipedal walker. The experimental results show that human intervention can accelerate the process of agent reinforcement learning during the training phase, and seek human help when guiding the dangerous state of the agent during the test phase. This is beneficial for solving real-world problems, further proving the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed framework and method.
Books
-
人机混合智能系统自主性理论和方法
赵云波,
康宇,
and 朱进
科学出版社
2021
[Abs]
[pdf]
人工智能(Artificial Intelligence, AI)技术的迅猛发展可能是科技领域近些年最为令人激动人心的现象之一。很少有一项具体的技术引发社会如此广泛的关注,除了技术专家,哲学、法律、道德、社会、管理、经济等各领域的专家学者都在其中各执一词,普通民众也同样表现出极大的热情,莫衷一是。这充分表现出AI技术对我们整个世界方方面面的巨大影响力,也预示着这一技术重塑我们整个世界的巨大潜力。 而谈及未来,一个与我们每个人都息息相关的话题就摆上桌面。在AI从业者那里,这一话题事关所谓的“强弱人工智能之辩”,其中的关键疑问是:现有的仅在某些方面强于人类的“专用人工智能”是否在未来会进化到在所有方面都强于人的“通用人工智能”?而在广大的民众那里,这一强弱人工智能之辩则关乎个人福祉甚至人类命运和尊严:高度发展的专用人工智能可以让创造性含量少的工作丢掉前景,而通用人工智能则更进一步会让整个人类失掉存在价值。这一话题早已在报刊、网络、电视各种公共舆论空间引发广泛的讨论,在真正的未来到来之前,激烈的讨论也远不会有消失的可能。 我们在此无需对这一充满科幻感的话题抛出我们的观点:从目前的技术发展现状来说,这一话题的讨论更多的出于信念,而非依据坚实的技术细节可以做出的可信技术展望。我们只强调如下的事实:AI技术的发展使得由其赋能的机器越来越具有更强大的智能自主能力,并且在越来越多的领域得到了应用,在可预见的未来AI技术的应用似乎还没有减速的迹象。 这一事实把一个原本并不存在或至少并不重要的问题推到了我们面前:在未来的世界里,人的智能和AI赋能的机器智能将无处不在的共存共生,如何在二者之间进行有效融合将成为科学研究的一个重要主题。 人的智能和机器智能在未来的融合共生正是本书的关注点,但本书的主题将更为具体的局限于自动化控制相关的技术领域中。我们认为,人的智能和机器智能在自动化控制领域的共融共存导致了所谓的“人机混合智能系统”的出现,这一新型的系统形式和智能形式在两方面具有本质的重要性:一方面,从自动化控制角度来说,人机混合智能系统所代表的系统结构形式是传统自动化控制系统应对AI赋能的机器智能变革的必然发展形式;另一方面,从智能科学的角度来说,人机混合智能系统所代表的智能形式也成为人工智能未来发展的重要甚至是唯一的终极形式。这两方面本质上的重要性使得建立相关领域的理论和方法框架变得极为急迫和重要。 在本书中,我们试图抛砖引玉,对这一全新而重要的研究领域提供虽然初步但仍然是系统的思考。我们并不希望过多执着于个人的自尊,浅薄地认为本书所提出的理论和方法是面向这一全新领域的必由之路;我们最大的愿望,不过是借由此书,谦卑地展示这一前景广阔而意义重大的研究领域,吸引更多的年轻学者投身其中。
Book Chapters
-
人机混合的智能控制
赵云波
In 智能控制:方法与应用
2020
[pdf]
patent
-
一种基于人的心理认知模型的青菜病害分类检测方法
赵云波,
赵丽丽,
花婷婷,
and 苏振岭
2024
[Abs]
[pdf]
一种基于人的心理认知模型提升分类器识别青菜病害的分类检测方法,含有以下步骤:步骤1:获取图像并对图像进行处理,获取多份病害区域、正常区域的青菜样本数据,分别以病害区域样本x1、x2为圆心画圆找出距离其最近的k个样本点;步骤2:分别计算最近的k个样本点中病害样本、正常样本所占的比例,并由此作出2×2列联表,表示样本x1、样本x2作为病害样本出现在最近邻的k个样本点中病害样本、正常样本中的概率;步骤3:结合步骤2所作列联表,利用人的松散对称模型再次计算样本x1、x2作为病害样本出现在最近邻的k个样本点中病害样本、正常样本中的概率;步骤4:把步骤3计算出的结果作为样本xi在分类器训练过程中的权重,这个值越大表示样本xi的精确度越高,越远离决策面,在决策中占的权重越高;步骤5:重复以上步骤确定其他病害样本和正常样本的权重并用SVM算法进行最终训练,根据不同样本的不同重要程度进行训练学习。步骤6:用训练好的SVM分类检测器对待检测的青菜进行病害检测。
-
一种基于POMDP和面部行为分析的驾驶培训辅助方法
赵云波,
吴芳,
赵丽丽,
and 崔奇
2024
[Abs]
[pdf]
本发明公开了一种基于POMDP和面部行为分析的驾驶培训辅助系统,包括步骤:实时采集学员的头部姿态、脸部表情以及眼睛注视图像,并对采集的图像进行处理;根据得到头部姿态、脸部表情和眼睛注视的图像,估计和预测学员的注意力情况;根据预测的学员的注意力情况和学员的操作结果给予学员适当的驾驶培训辅助提醒或控制。由于人的注意力等内部状态不能被完全直接观察到,只能通过互动和观察来推断,所以这类场景具有不完全可观测性。因此,本文以部分可观马尔可夫决策过程(Partially Observable Markov Decision Process, POMDP)为基础来实现驾驶培训辅助方法。本发明实现了在机器进行驾驶培训辅助的过程中实时地检测人的头部姿态、脸部表情以及眼睛注视,通过对学员的情绪和注意力的判断,基于POMDP实现驾驶辅助的最优决策,给学员提供合适的驾驶辅助输入,帮助学员获得更好的驾驶培训效果。
-
一种基于多算法集成的分歧介入珍珠分拣方法
赵云波,
花婷婷,
赵丽丽,
and 崔奇
2024
[Abs]
[pdf]
一种基于多算法集成的分歧介入珍珠分拣方法,含有:步骤1:将珍珠数据集按类别分别记为Class1-7,并给每张图片制定好标签,按6:2:2的比例分成训练集、验证集和测试集;步骤2:选取目前较为主流先进的三个模型ResNet50、SE-ResNet50和Vgg16进行独立训练,需均能够完成珍珠分拣任务,并分别保存最优模型;步骤3:将获取的三个最优模型用于仲裁系统,即针对构造后的主、次系统给出的预测结果进行分歧仲裁;步骤4:在实验验证阶段,我们使用分歧准确指数和额外成本指数作为系统分歧的评价指标,评估系统的整体性能;步骤5:根据步骤四的评价指标,选取既达到分拣精度提升较高又同时所需的人力成本较少的系统组合作为最终的珍珠分拣系统;步骤6:输出最终分类结果。本发明通过基于多个冗余算法的分歧找出机器分类可能存在的错误预测,并以最少的人力成本介入纠正其预测输出,从而提升整个珍珠分拣的分类精度。
-
一种人机系统中人的状态的识别方法
赵云波,
唐敏,
and 赵丽丽
2022
[Abs]
[pdf]
一种人机系统中人的状态的识别方法,含有:步骤 1 :传感器监测 T 至 T+1 时刻人的动作变化以及机器的输出并且汇集数据到处理器;步骤 2 :给分类器施 加权重对人的可能处于的状态进行分类,得到概率最大的状态 S K 机器概率 P K ; 步 骤 3 : T+1 时刻针对不同情况施加测试信号;步骤 4 :传感器监测 T+1 至 T+2 时刻 人的动作变化以及机器的输出并且汇集数据到处理器。步骤 5 :将处理后的数据 代入步骤 2 获得的以 P K 和 1-P K 为概率的二项分布中,计算其似然概率,得到人处 于 S K 状态的可能性。本发明解决了在一个人的状态未知但机器的输出可知的人 机系统中对人的状态识别的问题。
-
一种程序员的疲劳程度的检测方法
赵云波,
唐敏,
赵丽丽,
and 吴芳
2021
[Abs]
[pdf]
本发明的 一种程序员的疲劳程度的检测方法,包括:步骤 1 ,传感器监测 T 至 T+1 时刻程序员的头部动作变化以及键盘鼠标的输出并且汇集数据到处理器; 步骤 2 ,利用获得的人的头部动作变化以及键盘鼠标的输出,给分类器施加权重 对人的可能处于的状态进行分类,得到概率最大的状态 S K 机器概率 P K ;步骤 3 , T+1 时刻施加屏幕弹窗和提示音测试信号;步骤 4 ,传感器监测 T+1 至 T+2 时刻人 的头部动作变化以及键盘鼠标的输出并且汇集数据到处理器;步骤 5 ,代入二项 分布的公式进行计算,步骤二给出了一个可能的概率 P K ,把它看成是先验概率, 在步骤 3 和 4 的基础上进行更新。所以这里用贝叶斯公式进行更新。本发明能够 在一个程序员的状态未知但键盘和鼠标的输出可以获得的情况下的人机系统中 对程序员的疲劳程度识别。
-
一种基于多粒度特征与中层特征的分心驾驶检测方法
赵云波,
唐敏,
花婷婷,
and 赵丽丽
[Abs]
一种基于多粒度特征与中层特征的分心驾驶检测方法,含有:步骤1:训练融合多粒度特征与中层特征的分心驾驶检测神经网络;步骤2:运用该神经网络对Distracted–Driver–Detection数据集中的数据进行驾驶员注意力集中状况的测试;步骤3:针对步骤2中的测试结果的准确性来调整该神经网络的步长和学习率并再次进行测试直至测试结果的准确率符合条件;步骤4:通过车载终端摄像头实时获取驾驶员的驾驶状态并上传给训练好的该神经网络;步骤5:该神经网络对获取的图片进行识别后在车载终端显示分心驾驶行为。本发明通过车载终端获取驾驶员驾驶状态图像,上传给基于多粒度特征与中层特征的卷积神经网络CNN识别驾驶员分心驾驶行为。
-
一种基于图像的电脑操作员的疲劳检测方法
赵云波,
唐敏,
朱创,
and 孙悦铖
[Abs]
一种基于图像的电脑操作员的疲劳检测方法,含有以下步骤:步骤1:针对需要检测电脑操作员的疲劳状态的场景,拍摄照片构建“电脑操作员”数据集,并按照疲劳状态的类型把照片分类;步骤2:用CNN模型Resnet50模型对自建“电脑操作员”数据集中的训练集部分的数据进行训练,模型根据各张图片中电脑操作员的头部动作和面部特征各个像素点之间的距离关系来确定电脑操作员不同疲劳状态的类型的图片对应的特征;步骤3: 运用CNN模型Resnet50模型对自建“电脑操作员”数据集中的训练集部分的数据进行测试,模型根据步骤2中训练过程提取的图片中电脑操作员不同疲劳状态的类型的特征来判断测试集中给出的新的图片中的电脑操作员属于什么疲劳状态;步骤4:针对步骤3中的测试结果的准确性和来调整CNN模型Resnet50模型中的不同的元素对应的权重和步长的大小并再次进行测试直至测试结果的准确率符合条件; 步骤5:将参数调整后的CNN模型部署到带摄像头的计算机系统中运行;步骤6:通过摄像头实时获取电脑操作员的疲劳状态的类型并输出结果。发明通过布置深度学习环境并且调用电脑摄像头,实时获取电脑操作员的头部动作和面部特征,判断电脑操作员的的疲劳状态。
-
一种基于人的生理认知特点对苹果精细化分拣的分类方法
赵云波,
赵丽丽,
花婷婷,
and 苏振岭
[Abs]
一种基于人脑进行识别判断的脑部活动特征帮助支持向量机算法对苹 果进行精细化等级分拣的分类方法,含有以下步骤:步骤 1:获取人脑观看 识别苹果时的脑成像数据:通过核磁共振技术读取实验者对苹果进行分类 判断时的大脑活动,同时记录大脑活动和对应的视觉刺激(正在识别的苹 果的特征)之间的关联性。对大脑活动图像进行分析和处理,得到大脑皮 层进行识别判断时的图像数据;步骤 2:对脑成像数据进行处理,获得判断 颜色红、个头大且形状规则的苹果的积极活动因子α:对步骤 1 获得的图 像数据预处理,提取脑部在识别刺激类型时的活动特征,作为积极活动因 子α;步骤 3:直接运用带有颜色红、个头大且形状规则和颜色青、个头小 且形状不规则的图片对支持向量机算法进行训练,利用惩罚函数 HL 调整 决策边界;步骤 4:把步骤 2 中人脑识别中的积极活动因子的影响带入到 步骤 3 的调整决策边界的过程中,当判断有误时加大惩罚的力度,进一步 优化调整决策边界;步骤 5:用训练好的分类器对样本进行分类。本发明涉 及一种基于人的生理认知特点对苹果精细化分拣的分类方法,这种生理认 知在此被认为是人脑进行识别判断的脑部活动特征,此方法适用于果农针 对不同品质的苹果分级销售时使用人工分拣成本较高的情况。
-
一种基于图像的驾驶员注意力检测方法
赵云波,
唐敏,
吴芳,
and 赵丽丽
[Abs]
本发明的一种基于图像的驾驶员注意力检测方法,含有:步骤1:用轻量化的CNN模型对Distracted – Driver – Detection数据集中的数据进行训练,以提取驾驶员注意力不同情况对应的特征;步骤2:运用该CNN模型对Distracted–Driver–Detection数据集中的数据进行驾驶员注意力集中状况的测试;步骤3:针对步骤2中的测试结果的准确性来调整CNN模型中的权重和步长并再次进行测试直至测试结果的准确率符合条件;步骤4:将参数调整后的CNN模型部署到嵌入式系统中运行;步骤5:通过摄像头实时获取驾驶员的注意力集中状态并输出结果。本发明利用轻量化的CNN模型实时获取驾驶员的注意力集中情况,进行驾驶员的注意力集中状态的检测。
项目人员
赵云波 吴芳 唐敏 张倩倩 游诗艺 王岭人 花婷婷 赵丽丽

